Script Runner: A Plugin to Run Python Scripts in QGIS
Following up on my last post, Running Scripts in the Python Console, I created a plugin to simplify running scripts:
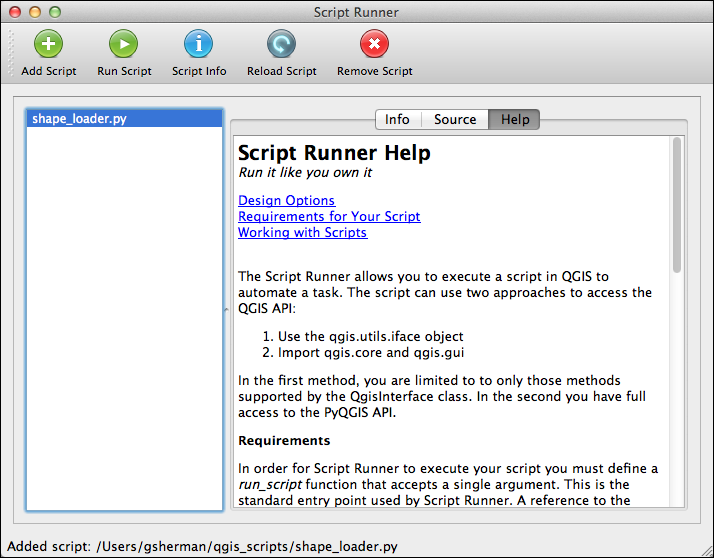
The Script Runner plugin allows you to add your scripts to a list so they are readily available. You can then run them to automate QGIS tasks and have full access to the PyQGIS API. In addition, you can view information about the classes, methods, and functions in your module as well as browse the source:
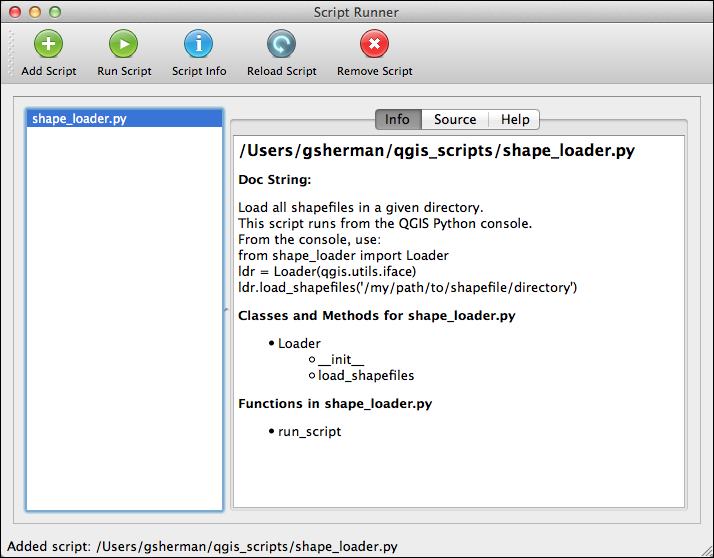
In order for your script to work with ScriptRunner it has to implement a single function as an entry point. Here is some additional information from the Help tab of the plugin:
Requirements
In order for Script Runner to execute your script you must define a run_script function that accepts a single argument. This is the standard entry point used by Script Runner. A reference to the qgis.utils.iface object will be passed to your run_script function. You don't have to use the iface object in your script but your run_script function must accept it as an argument.
Here is an example of a simple run_script function:
def run_script(iface):
ldr = Loader(iface)
ldr.load_shapefiles('/vmap0_shapefiles')In this example, the run_script creates an instance (ldr) of a class named Loader that is defined in the same source file. It then calls a method in the Loader class named load_shapefiles to do something useful---in this case, load all the shapefiles in a specified directory.
Alternatively, you could choose not to use classes and just do everything within the run_script function, including having it call functions in the same script or others you might import. The important thing is to be sure you have defined a run_script function. If not, Script Runner won't load your script.
Working with Scripts
To run a script, you must add it to Script Runner using the Add Script tool on the toolbar. This will add it to a list in the left panel. This list of scripts is persisted between uses of QGIS. You can remove a script using the Remove Script tool. This just removes it from the list; it does nothing to the script file on disk.
Once you have a script loaded, you can click the Script Info tool to populate the Info and Source tabs in the panel on the right. The Info tab contains the docstring from your module and then a list of the classes, methods, and functions found in the script. Having a proper docstring at the head of your script will help you determine the puprose of script.
You can view the source of the script on the Source tab. This allows you to quickly confirm that you are using the right script and it does what you think it will.
Installing the Plugin
To install the plugin:- Open the Python plugin installer: Plugins->Fetch Python Plugins
- Check to see if you have the new Official repository in your list of plugins by clicking on Repositories tab. The URL is http://plugins.qgis.org/plugins/plugins.xml.
- If you have it, skip to step 5. If the new repository isn't in the list, add it by clicking the Add button. Give it a name and insert the URL http://plugins.qgis.org/plugins/plugins.xml
- Click on the Plugins tab
- Enter scriptrunner in the Filter box
- Select the ScriptRunner plugin and click Install
ScriptRunner adds an entry to the Plugins menu as well as a tool on the Plugins toolbar: <img style=“vertical-align:middle” src="/images/icon.png" alt="" title=“icon” width=“32” height=“32” align=“absmiddle” size-full wp-image-844" />
Click it and you are off and running.
