QGIS Plugin of the Week: OpenLayers
This week we look at the OpenLayers plugin for QGIS. This plugin allows you to add a number of image services to your map canvas:
- Google
- Physical
- Streets
- Hybrid
- Satellite
- OpenStreetMap
- Yahoo
- Street
- Hybrid
- Satellite
- Bing
- Road
- Aerial
- Aerial with labels
Installing the Plugin
The OpenLayers plugin is installed like all other Python plugins. From the the Plugins menu in QGIS, choose Fetch Python Plugins. This brings up the plugin installer. To find the plugin, enter openlayers in the Filter box, then select OpenLayers Plugin from the list. Once it’s highlighted, click the Install plugin button. This will download the plugin from the repository, install it, and load it into QGIS.
Using the Plugin
The OpenLayers Plugin uses your view extent to fetch the data from the service you choose. For this reason you should load at least one of your own layers first. Since each of the services are expecting a request in latitude/longitude your layer either has to be geographic or you must enable on the fly projection.
To add one of the services you have two choices; you can pick the service from the Plugins->OpenLayers plugin menu or you can use the OpenLayers Overview. The Overview opens a new panel that allows you to choose a service from a drop-down list. Click the Enable map checkbox to enable the drop-down list and preview the service you want to add. If you are happy with what you see, you can add it to the map by clicking the Add map button.
In the screenshot below we have enabled the Overview panel, added the world boundaries layer[1], zoomed to an area of interest, and added the Google terrain (physical) data:
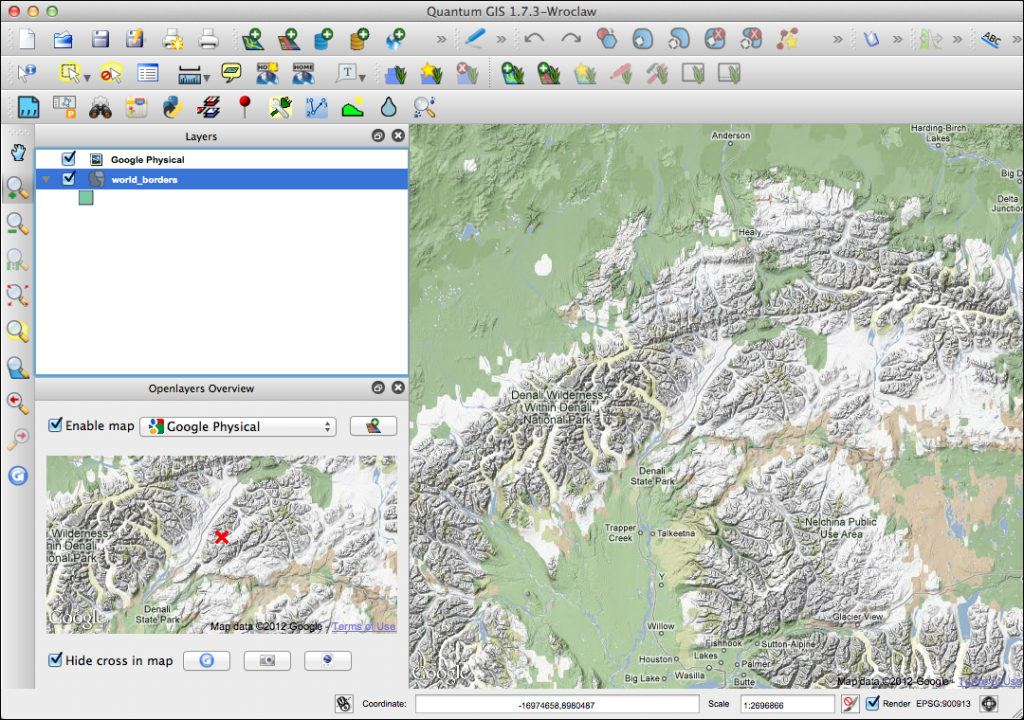
You can add as many services as you want, previewing them using the OpenLayers Overview panel.
[1] You can get the world boundaries layer from the Geospatial Desktop sample data set.
